SKIN CHECK your MOLES for MELANOMA
BENIGN ‘MOLES’ (*here I define a mole as any pigmented lesion seen on the skin) do CHANGE
Seborrhoeic keratoses/warts also score using the ABCDE check list (asymmetry, border, colour, diameter, evolution) so the presence of these features does not necessarily mean the lesion is malignant.
A DARK area in a mole with a SMOOTH surface is a more useful sign that the mole should be
checked by a dermatologist or doctor.
Early MELANOMAS are SMOOTH & DARK (the SaD mole)
NOT DARK
Benign
The Good |
Melanoma
(Dysplastic naevus)
The BAD |
NOT SMOOTH
Benign
The UGLY |
| |
|
|
If a mole is SMOOTH and DARK, then use the ABCD checklist.
The pigment cells in a melanoma start to spread outwards first in an irregular manner:
(this results in an increase in size/area, with an irregular border and irregularity in colour as well as becoming darker). SCORE 2 to diagnose dysplastic naevus and SCORE 3+ to diagnose a melanoma.
(A=Asymmetry not used = irregular shape or colour, A for area instead of diameter and D for dark)
A = Area
Larger than
end of a pencil |
B = BORDER
Irregular |
C = COLOUR
2 or more |
D = DARK
Part of lesion
dark brown or black
|
 |
 |
 |
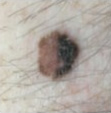 |
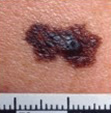
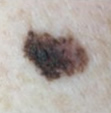
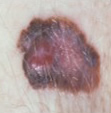
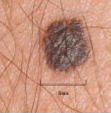
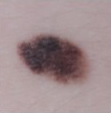
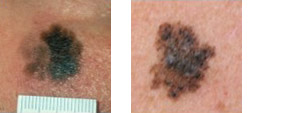
Examples of ABCD scores
 |
 |
 |
ABCD = 1
dark
(junctional naevus)
|
ABCD = 2
dark 2 colours
(dysplastic naevus)
|
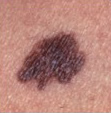
ABCD = 4 ABCD = 4
> pencil, border jagged, 2 colours, dark
(malignant melanoma) (malignant melanoma)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
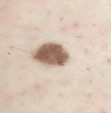
ABCD = 2
> pencil, jagged bdr
(solar lentigo) |
ABCD = 2
jagged, dark
(dysplastic naevus) |
ABCD = 0
(benign naevus) |
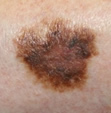
ABCD = 4
all features +ve
(Lentigo maligna) |
BENIGN MOLES (present from childhood may also have a smooth surface)
These may change by getting LIGHTER and ELEVATED over time through 3 stages:
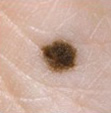
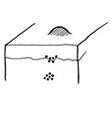
| a. JUNCTIONAL NAEVUS |
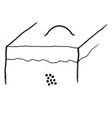
b. COMPOUND NAEVUS |
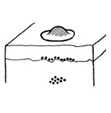
c. INTRADERMAL NAEVUS |
COMBINED JUNCTIONAL & COMPOUND NAEVUS |
| Clinical features:- |
|
|
|
 |
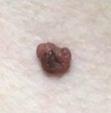 |
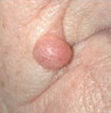 |
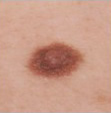 |
| Flat & dark brown |
Raised and lighter brown
|
Raised (dome shaped or papillomatous) & skin coloured. |
Periphery flat & brown,
centre raised & brown |
| Histological features:- |
|
|
|
| Naevus cells at dermo-epidermal junction. |
Naevus cells at dermo-epidermal junction and within the dermis. |
Naevus cells only within dermis. |
Junctional cell throughout lesion, intradermal cell centrally only. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
MALIGNANT MELANOMA
Early melanoma has a SMOOTH surface and is usually DARK, a ‘SaD mole’, and scores 3+ points on the ABCD check list (see before).
In-SITU MELANOMA is a melanoma-in-waiting. The malignant cells are only in the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) so cannot spread anywhere else. If removed, then it is 100% cured.
Lentigo maligna occurs in the elderly on sun damaged skin, is slow growing with malignant cells seen in the epidermis only.
SUPERFICIAL SPREADING MELANOMA has also a SMOOTH surface and is usually DARK. There is invasion of malignant melanocytes into the dermis, the thickness of the melanoma is less than 1-2mm. There is a possibility of spread but this is low.
NODULAR MELANOMAS occur at a later stage, especially if the early flat and dark lesions are not recognised. More rarely they can grow spontaneously as a nodule.
Nodular melanomas can be GROWING RAPIDLY and DARK, the ‘GRaD moles’
or be BLEEDING and DARK, the ‘BaD moles’
GRaD moles (growing rapidly and dark) change over a period of weeks or months.
BaD moles (bleeding and dark) also grow rapidly and then ulcerated and bleed.
AMELANOTIC MELANOMAS cannot be diagnosed easily because they are NOT DARK. They usually are a growing rapidly smooth/ulcerated nodule which is pink or red in colour. They need to be biopsied before a diagnosis can be made to differentiate them from a squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), dermal metastasis or a lymphoma.
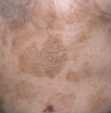
SEBORRHOEIC KERATOSIS/WART have warty or crumbly surface situated on top of the surface (in someone usually over age 50 years). They may look worrying but are harmless.
NON-MELANOMA SKIN CANCERS
If there is an ULCER OR BLEEDING
consider a basal cell carcinoma unless the
lesion has been present for less than 4
months (it might be a squamous cell
carcinoma or an amelanotic melanoma). |
Is there a RAPIDLY GROWING LUMP
present for less than 4 months. It it has a horny
rough/hard surface, it is a squamous cell
carcinoma. If it has a smooth surface it could be an SCC, amelanotic melanoma or a lymphoma.
|
| These images are basal cell carcinomas |
These are squamous cell carcinomas
|
|

